GATE Previous Year Wise Questions
gate 2018
GATE 2019
gate 2016
gate 2016 set 1
GATE 2017 SET 1
GATE 2017 SET2
GATE 2015 SET 1
GATE 2015 SET 2
GATE 2015 SET3
GATE 2014 SET 1
GATE 2014 SET 2
GATE 2013
gate 2009
GATE 2012
gate 2010
GATE 2019
GATE 2014 SET 3
gate 2011
GATE 2008 CS
GATE 2008 IT
GATE 2007 CS
GATE 2007 IT
GATE 2006 CS
GATE 2006 IT
GATE 2005 CS
GATE 2005 IT
GATE 2004 CS
GATE Previous Subject Wise Questions
Data Structures
Algorithms
operating systems
computer organization
Computer Networks
DBMS
Graph Theory
Question 81
Which one of the following is the recurrence equation for the worst case time complexity of theQuicksort algorithm for sorting n ( ≥ 2) numbers? In the recurrence equations given in the options
below, c is a constant.
A
T(n) = 2 T(n/2) + cn
B
T(n) = T(n − 1) + T(1) + cn
C
T(n) = 2T(n − 1) + cn
D
T(n) = T(n/2) + cn
Algorithms
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 82
The height of a tree is the length of the longest root-to-leaf path in it. The maximum and minimumnumber of nodes in a binary tree of height 5 are
A
63 and 6, respectively
B
64 and 5, respectively
C
32 and 6, respectively
D
31 and 5, respectively
Data Structures
GATE 2015 SET 1
Trees
Question 83
Which of the following is/are correct inorder traversal sequence(s) of binary search tree(s)?I. 3, 5, 7, 8, 15, 19, 25
II. 5, 8, 9, 12, 10, 15, 25
III. 2, 7, 10, 8, 14, 16, 20
IV. 4, 6, 7, 9 18, 20, 25
A
I and IV only
B
II and III only
C
II and IV only
D
II only
Data Structures
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 84
For computers based on three-address instruction formats, each address field can be used to specifywhich of the following:
(S1) A memory operand
(S2) A processor register
(S3) An implied accumulator register
A
Either S1 or S2
B
Either S2 or S3
C
Only S2 and S3
D
All of S1, S2 and S3
computer organization
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 85
Suppose two hosts use a TCP connection to transfer a large file. Which of the following statementsis/are FALSE with respect to the TCP connection?
I. If the sequence number of a segment is m, then the sequence number of the subsequent
segment is always m+1.
II. If the estimated round trip time at any given point of time is t sec, the value of the
retransmission timeout is always set to greater than or equal to t sec.
III. The size of the advertised window never changes during the course of the TCP connection.
IV. The number of unacknowledged bytes at the sender is always less than or equal to the
advertised window.
A
III only
B
I and III only
C
I and IV only
D
II and IV only
Computer Networks
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 86
Which one of the following fields of an IP header is NOT modified by a typical IP router?
A
Checksum
B
Source address
C
Time to Live (TTL)
D
Length
Computer Networks
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 87

Submit
operating systems
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 88
SELECT operation in SQL is equivalent to
A
the selection operation in relational algebra
B
the selection operation in relational algebra, except that SELECT in SQL retains duplicates
C
the projection operation in relational algebra
D
the projection operation in relational algebra, except that SELECT in SQL retains duplicates
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 89
What are the worst-case complexities of insertion and deletion of a key in a binary search tree?
A
θ (log n ) for both insertion and deletion
B
θ ( n) for both insertion and deletion
C
θ (n ) for insertion and θ (log n ) for deletion
D
θ (logn ) for insertion and θ (n ) for deletion
Algorithms
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 90
Suppose that the stop-and-wait protocol is used on a link with a bit rate of 64 kilobits per secondand 20 milliseconds propagation delay. Assume that the transmission time for the
acknowledgement and the processing time at nodes are negligible. Then the minimum frame size in
bytes to achieve a link utilization of at least 50% is______________.
Submit
Computer Networks
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 91

Now consider that a value 35 is inserted into this heap. After insertion, the new heap is
A
40, 30, 20, 10, 15, 16, 17, 8, 4, 35
B
40, 35, 20, 10, 30, 16, 17, 8, 4, 15
C
40, 30, 20, 10, 35, 16, 17, 8, 4, 15
D
40, 35, 20, 10, 15, 16, 17, 8, 4, 30
Data Structures
GATE 2015 SET 1
Heap-Tree
Question 92

Submit
Computer Networks
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 93
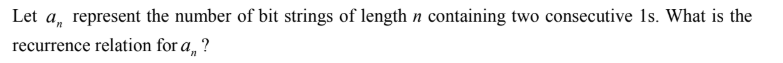
A
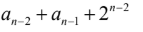
B
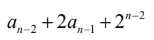
C
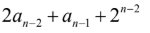
D
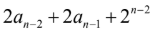
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 94

A
-1
B
0
C
1
D
2
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 95
Consider a uniprocessor system executing three tasks T1, T2 and T3, each of which is composed ofan infinite sequence of jobs (or instances) which arrive periodically at intervals of 3, 7 and 20
milliseconds, respectively. The priority of each task is the inverse of its period, and the available
tasks are scheduled in order of priority, with the highest priority task scheduled first. Each instance
of T1, T2 and T3 requires an execution time of 1, 2 and 4 milliseconds, respectively. Given that all
tasks initially arrive at the beginning of the 1st millisecond and task preemptions are allowed, the
first instance of T3 completes its execution at the end of _____________ milliseconds.
Submit
operating systems
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 96
Consider a disk pack with a seek time of 4 milliseconds and rotational speed of 10000 rotations perminute (RPM). It has 600 sectors per track and each sector can store 512 bytes of data. Consider a
file stored in the disk. The file contains 2000 sectors. Assume that every sector access necessitates a
seek, and the average rotational latency for accessing each sector is half of the time for one
complete rotation. The total time (in milliseconds) needed to read the entire file is ____________.
Submit
operating systems
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 97
Consider a non-pipelined processor with a clock rate of 2.5 gigahertz and average cycles perinstruction of four. The same processor is upgraded to a pipelined processor with five stages; but
due to the internal pipeline delay, the clock speed is reduced to 2 gigahertz. Assume that there are
no stalls in the pipeline. The speed up achieved in this pipelined processor is_________.
Submit
computer organization
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 98
Suppose the following disk request sequence (track numbers) for a disk with 100 tracks is given:45, 20, 90, 10, 50, 60, 80, 25, 70. Assume that the initial position of the R/W head is on track 50.
The additional distance that will be traversed by the R/W head when the Shortest Seek Time First
(SSTF) algorithm is used compared to the SCAN (Elevator) algorithm (assuming that SCAN
algorithm moves towards 100 when it starts execution) is____________ tracks.
Submit
operating systems
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 99
Consider a main memory with five page frames and the following sequence of page references: 3,8, 2, 3, 9, 1, 6, 3, 8, 9, 3, 6, 2, 1, 3. Which one of the following is true with respect to page
replacement policies First In First Out (FIFO) and Least Recently Used (LRU)?
A
Both incur the same number of page faults
B
FIFO incurs 2 more page faults than LRU
C
LRU incurs 2 more page faults than FIFO
D
FIFO incurs 1 more page faults than LRU
operating systems
GATE 2015 SET 1
Question 100

A
Unsorted array
B
Min-heap
C
Sorted array
D
Sorted doubly linked list
Algorithms
GATE 2015 SET 1
Time-Complexity
© 2026 - All rights are reserved- AAIC Technologies pvt ltd

